Identify the 3 types of Australian black cockatoos of South West WA
There are 3 types of Australian black cockatoos found in the southwest corner of Western Australia and in Perth, Australia. They are:
- The Forest Red-Tailed Black Cockatoo
- The Carnaby’s Black Cockatoo
- The Baudin’s Black Cockatoo
All of them are under threat of extinction due to habitat loss, conflict with humans, illegal poaching & shooting, poisoning, competition with other species such as corellas and galah and feral bees.
Cockatoos are a family of large (approx. 60 m), long-lived and very noisy parrots with moveable crests. Australia is home to 14 species with others also found in Papua New Guinea, Indonesia, the Solomon Islands and the Philippines.
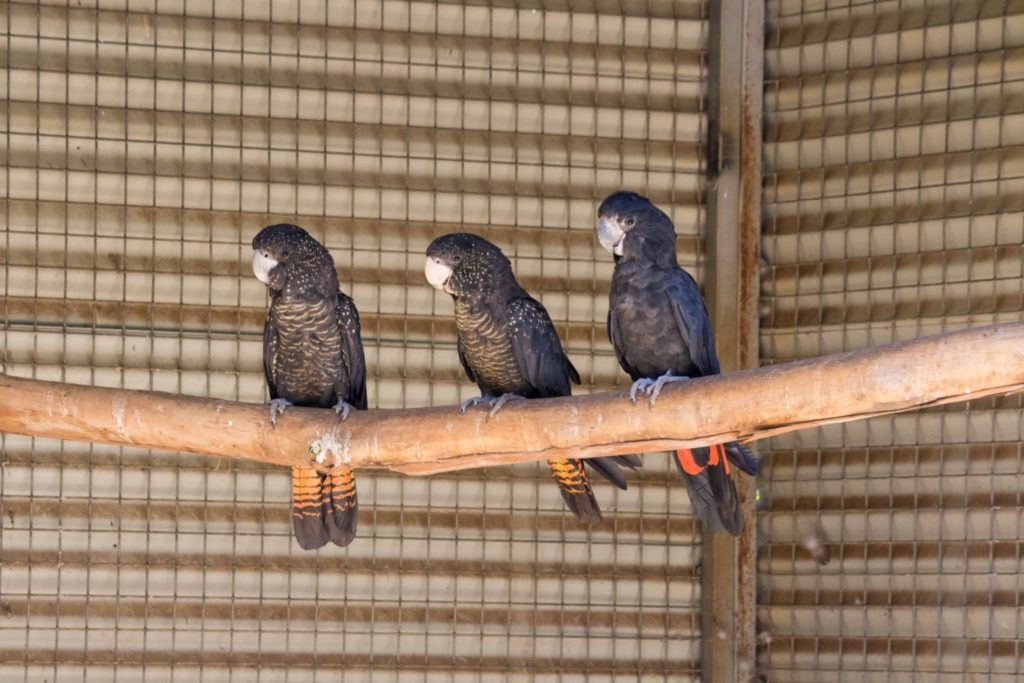
Black cockatoos are mostly black, but they can sometime appear brownish or grey in different lighting conditions. They are very social birds and you will often see them in pairs (families), small groups or large flocks. They communicate a lot and you can hear them well before you see them!
Different habitats
Carnaby’s cockatoos inhabit low heaths of the Midwest and south coast, while Baudin’s and Forest Red-Tailed Black Cockatoos have a preference for jarrah and marri forests. However, red tails cockatoos can now be frequently seen in the city due to their newly adaptation at eating non-native seeds and the fact that they are running out of places to live due to deforestation.
Ravens or black cockatoo?
In the sky, ravens have much faster wing beats while black cockatoos have slowed and long wing beats. Black cockatoos have a rounded bill while ravens have a sharp beak.
How many species of black cockatoos are there in total in Australia?
In Australia, there are 5 species of black cockatoos:
- The Red-Tailed Black Cockatoo
- The Carnaby’s Black Cockatoo
- The Baudin’s Black Cockatoo
- The Glossy Black Cockatoo
- The Yellow-Tailed Black Cockatoo
The Forest Red Tailed Cockatoo is a sub-species of the Red Tail Cockatoo.
Five subspecies are recognised in Australia. They differ mainly in the size and shape of the beak, the overall bird size and female colouration:
- b. banksiiis found in Queensland and, rarely, in far northern NSW.
- b. graptogyne, (Endangered)known as the south-eastern red-tailed black cockatoo, is found in southwestern Victoria and southeastern South Australia. Less than 1,000 cockatoos is found in the wild.
- b. macrorhynchusis found across Northern Australia. It is large and has a large beak.
- b. naso (Near Threatened) is known as the forest red-tailed black cockatoo and is found in the southwest corner of Western Australia between Perth and Albany. “Naso” means the cockatoo has a large bill. This species was named by was named by John Gould in 1837.They are Known to the Noongar people as ‘Karrak’.
- b. samueli in central coastal Western Australia from the Pilbara south to the northern Wheatbelt in the vicinity of Northam, and inland river courses in Central Australia, southwestern Queensland and the upper Darling River system in Western New South Wales. Samueli are smaller than other sub-species of red tail cockatoos.
The red-tailed black cockatoo’s closest relative is the glossy black cockatoo.
Are black cockatoo endangered?
- The glossy black-cockatoos are one of the more threatened species of cockatoo in Australia and are listed as a vulnerable in NSW.
- Carnaby’s black-cockatoos are listed as endangered in WA.
- Baudin’s black-cockatoos are listed as endangered in WA.
- The Yellow-Tailed black-cockatoos are listed as vulnerable in SA, and secure in NSW, QLD, TAS, ACT and VIC.
- Red-Tailed black-cockatoos:
- b. graptogyne is listed as endangered.
- naso (Forest Red-Tailed black-cockatoo) is listed as vulnerable (near-threatened)
According to the 2019 Great Cocky Count:
“Despite a recent stabilisation of the local population, the trend since 2010 shows a 35% decline of Carnaby’s and a 13% decline per year of Baudin’s. A precautionary approach dictates that efforts be made to protect remnant vegetation of Black-Cockatoos, particularly Banksia woodlands and Marri/Jarrah forest. Revegetation of former pine plantations should be a priority to ensure no feed gap in the future.”
How many black cockatoos are left in the wild?
Below are estimates of the numbers of black cockatoos left in the wild in our region:
- Carnaby’s cockatoos: Estimated numbers of 40,000.
- Baudin’s cockatoos: Estimated numbers of 12,000.
- Forest Red Tail cockatoos: Estimated numbers of 15,000.
If you would like to know more about the threats that black cockatoos face, please visit our “Black Cockatoo Threats” page.
How to identify the three types of black cockatoos found nowhere else in the world?
There are many ways to identify the black cockatoos:
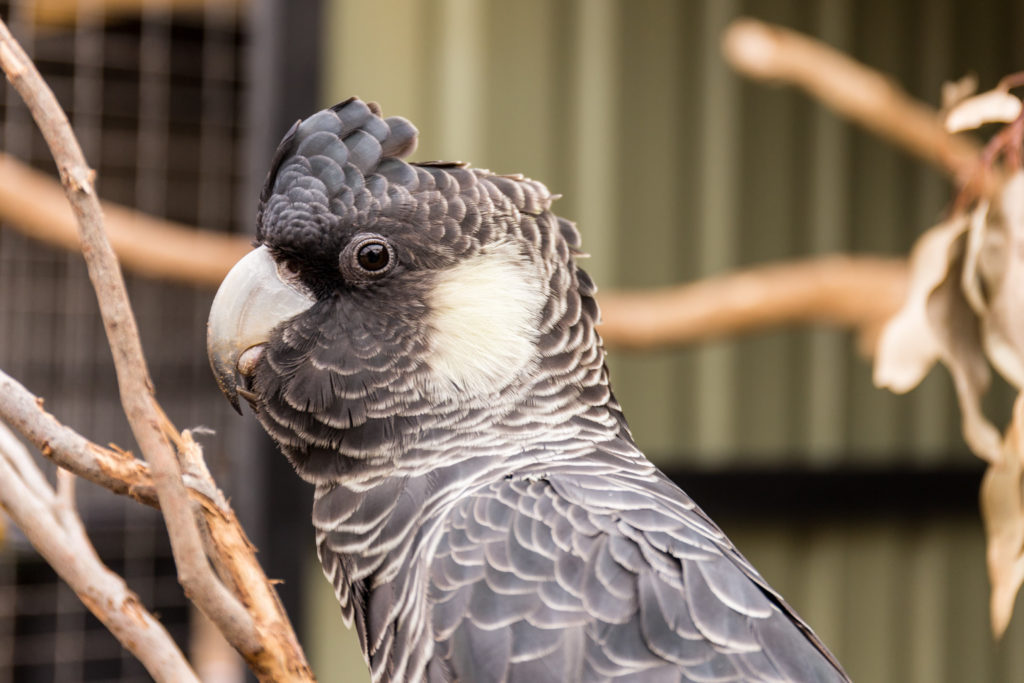
- Visual identification (look for the black cockatoo feathers, the bill ant the ear patch)
- Calling sound (What do black cockatoo sound like?)
- How they chew marri nuts
Forest Red Tail Cockatoo
Forest Red Tail Cockatoos are commonly called red tailed black cockatoos in Perth. They are easily identified by their bright red tail.
Male forest red tails have bright orange-red band in the tail and their bill is dark grey or blackish.
Females have their head and wings spotted with pale yellow. Their breast and belly are barred with orange yellow. Their tail is narrowly banded with orange-yellow and their bill is pale greyish white.
Juvenile males resemble adult females until about three years old.

Forest Red Tail Cockatoo calling sound
Forest Red Tail cockatoos have loud harsh cries described as “Karee”, “Karrak” or “Krar-raak” also “chet” sounds and harsh nasal wheezing. Male breeding call is a repeated mechanical “waa-waa” (with the crest up).
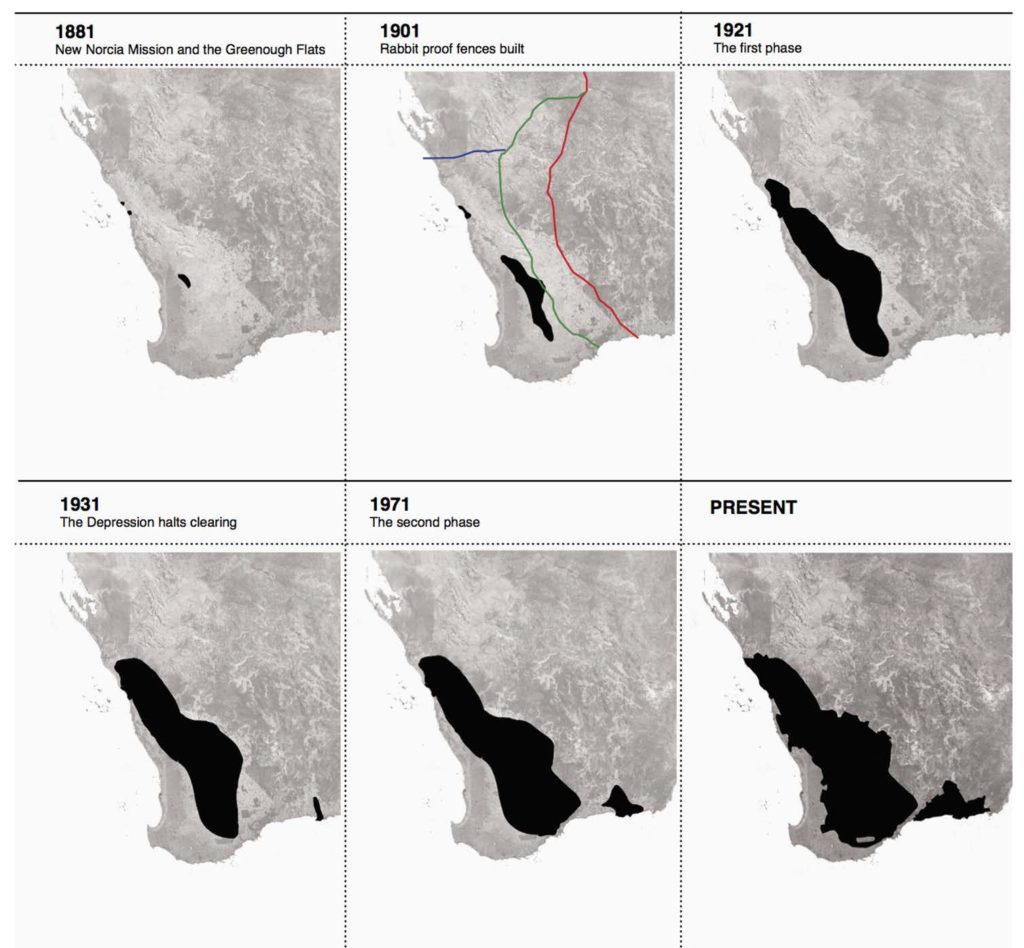
Forest Red Tail Cockatoo chewing marks
Learn more about the Forest Red-Tailed Cockatoo.
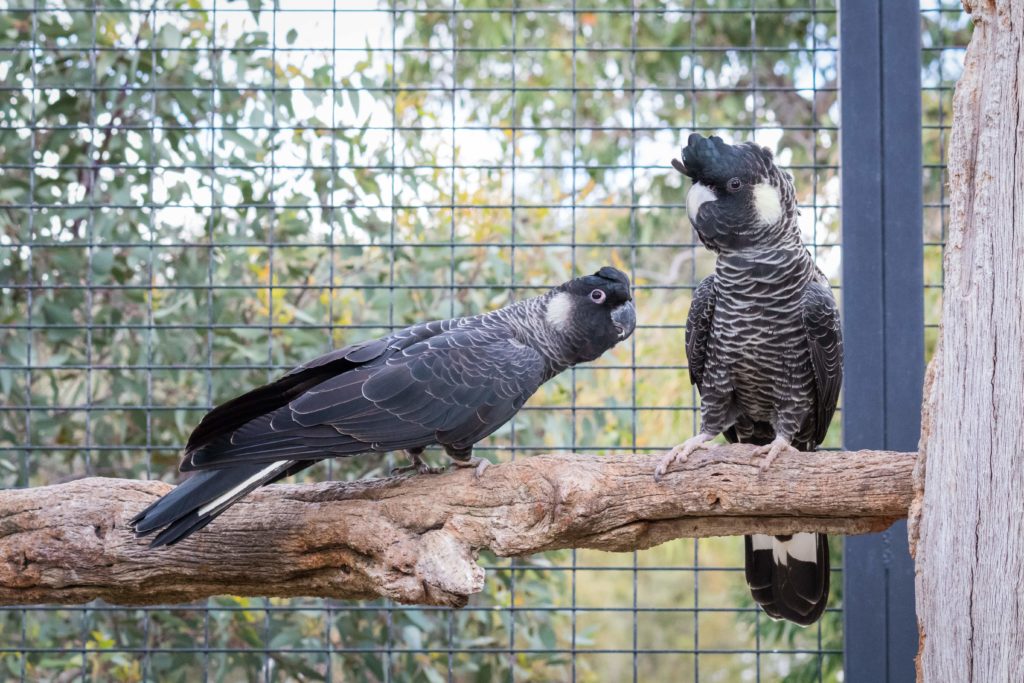
Carnaby’s black cockatoos
Carnaby’s cockatoos are considered as iconic birds in Southwest WA. They are commonly called “white tailed black cockatoos”. They can easily be mistaken with the other species of black cockatoos found in the southwest corner of Western Australia: the Baudin’s cockatoo. Carnaby’s black cockatoos have a bright white band in the tail.
Male Carnaby’s cockatoos have a black bill, pink eye ring and dusky white ear patch.
Females have a greyish white bill, grey eye ring and yellowish white ear patch.
Juvenile males resemble adult females until about three years old. They look hunched and their cover their beak with feathers.

Carnaby’s Cockatoo calling sound
The voice is generally noisy with several calls; loudest and most frequent is a wailing “wy-lah”.
The male’s breeding call is different and can be perceived as a whistle and “ah” “ah” sounds. Nestlings and young baby black cockatoos make a noisy grating begging call when seeking or expecting food.
The call of the Carnaby’s cockatoo is longer than the Baudin’s cockatoo call.
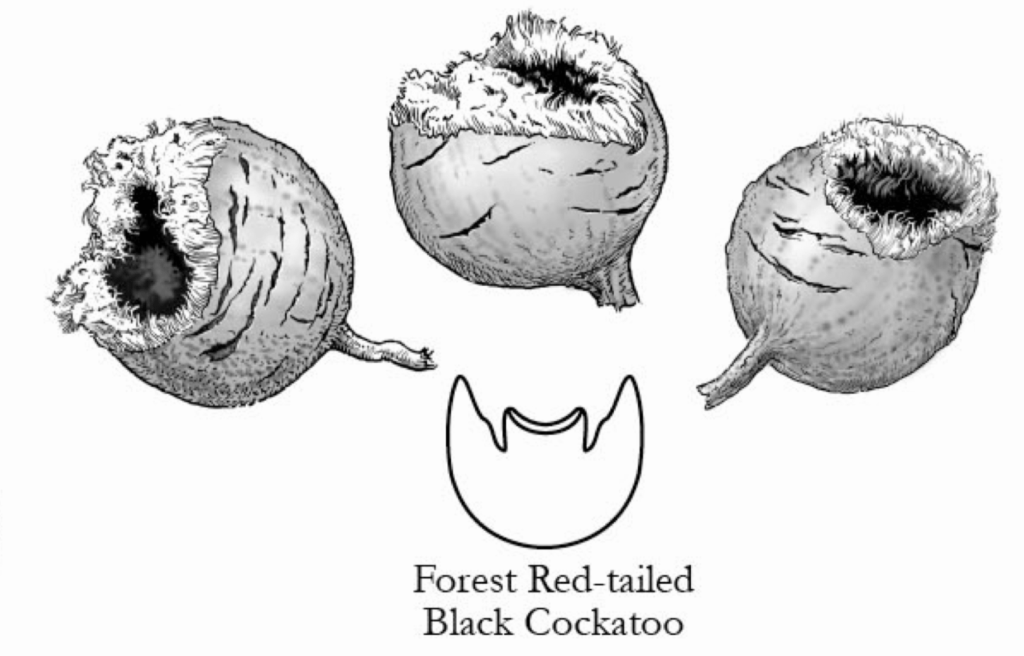
Carnaby’s Cockatoo chewing marks
Learn more about the Carnaby’s Cockatoo.
Baudin’s Black Cockatoo
Baudin’s cockatoos are easily mistaken for Carnaby’s black cockatoos. They look very similar- Both have white tails and cheek patches but Carnaby’s cockatoos have a shorter upper beak.
Baudin’s have a longer bill and their calling sound is different. Their habitat is slightly different from the Carnaby’s black cockatoo.
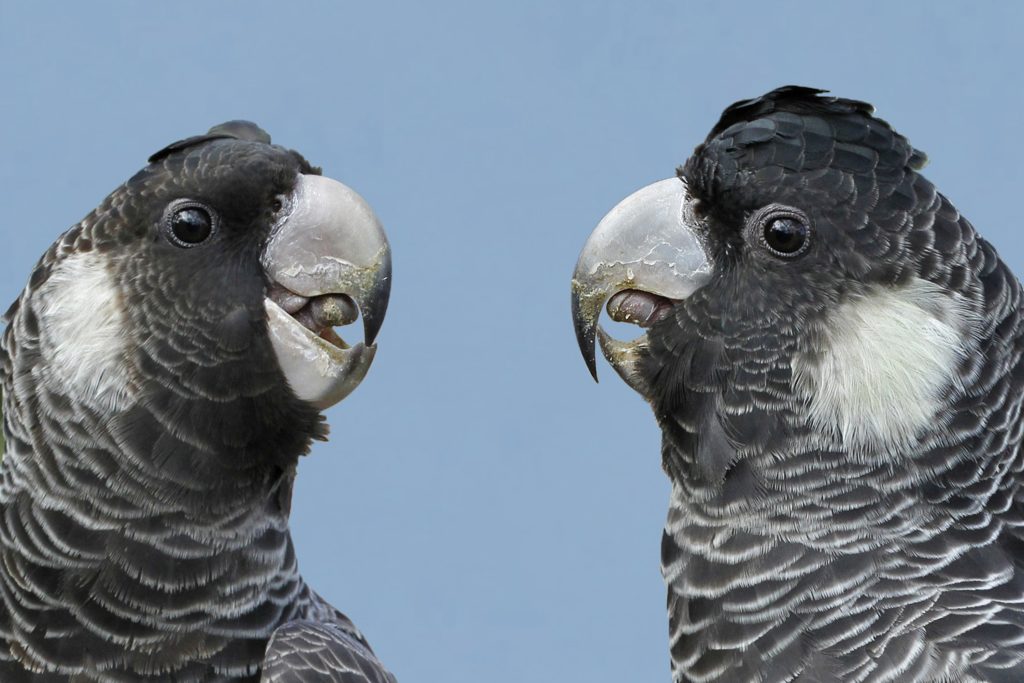

Males have a black bill, pink eye ring and dusky white ear patch.
Females have a greyish white bill, grey eye ring and yellowish white ear patch.
Juvenile males resemble adult females until about three years old.
Baudin’s Cockatoo calling sound
Their calling sounds like “bunyip-bunyip” or “whichea-whichea”. Their call is often repeated and is shorter than the Carnaby’s cockatoo call.
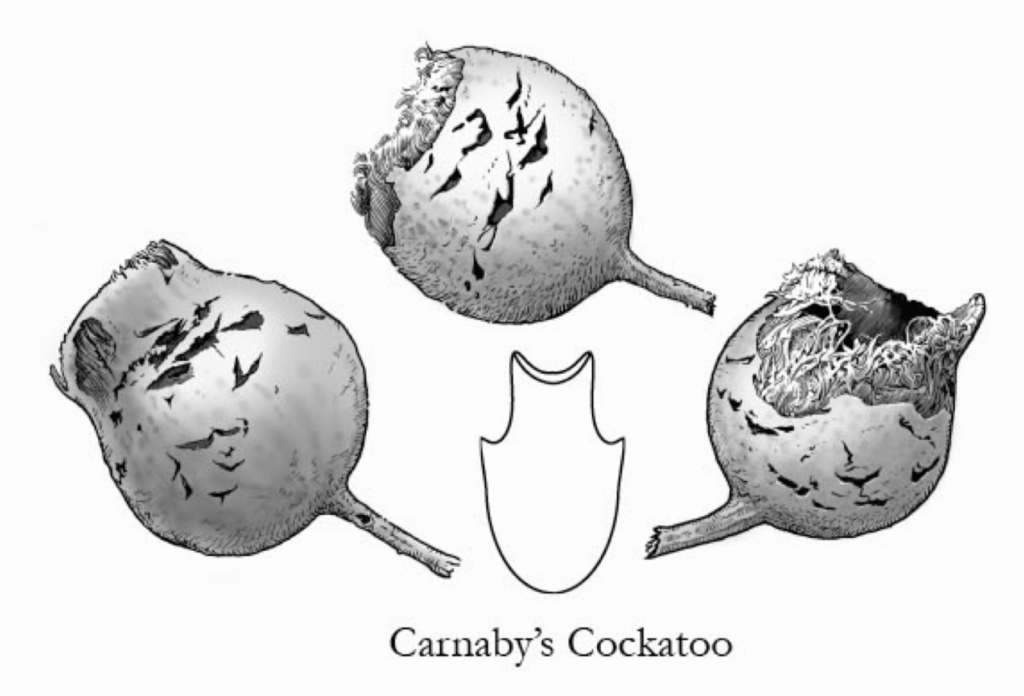
Baudin’s Cockatoo chewing marks
Learn more about the Baudin’s Cockatoo.
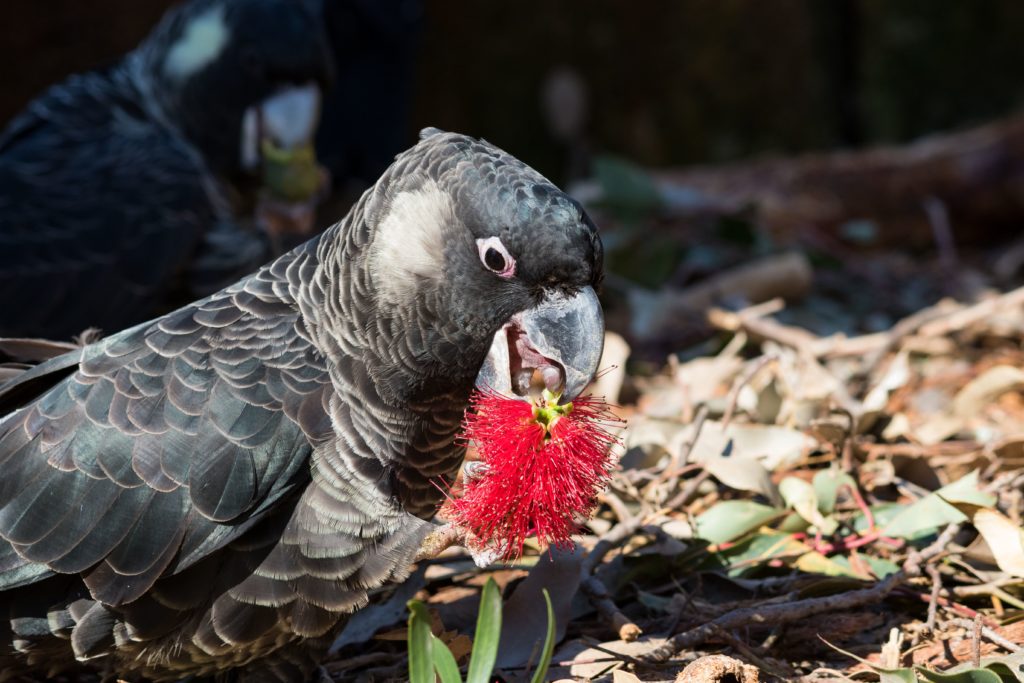
What do black cockatoos eat?
Carnaby’s cockatoos like to eat the seeds of Marri, Banksia, Hakea, Eucalyptus and Grevillia plants but they also enjoy eating pinecones (they adapted to eat this non-native food), nectar from flowers and insect larvae.
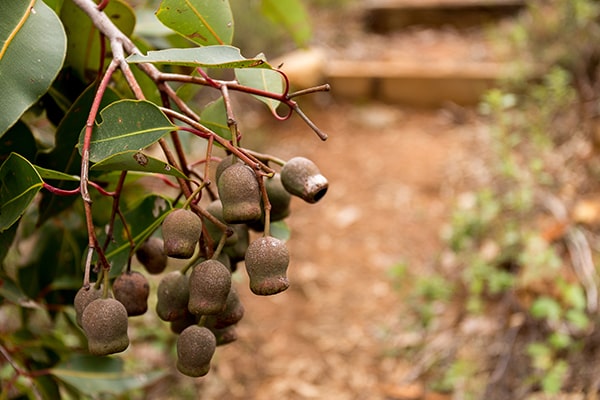

Pinecones are considered “junk food” as they provide a lot of calories.
Red Tailed Black Cockatoos eat the seeds of Marri, Jarrah, Blackbutt, Karri, Sheoak and Snottygobble, also some ornamental eucalypts and introduced Cape Lilac.
Baudin’s cockatoos like to eat the seeds and flowers of Marri, Banksia, Hakea and Jarrah trees but they also enjoy eating apples and pears, which bring them to trouble with orchardists.
Choose friendly black cockatoo plants for your garden
DBCA has published a very thorough guide on which plants are best for the Carnaby’s cockatoo.
We recommend visiting your local nursery to find what’s available and receive personalised advice.
Below is a list of black cockatoo friendly plants. Click on the tabs:
This small library is under construction. If you would like to contribute, please get in touch with us.
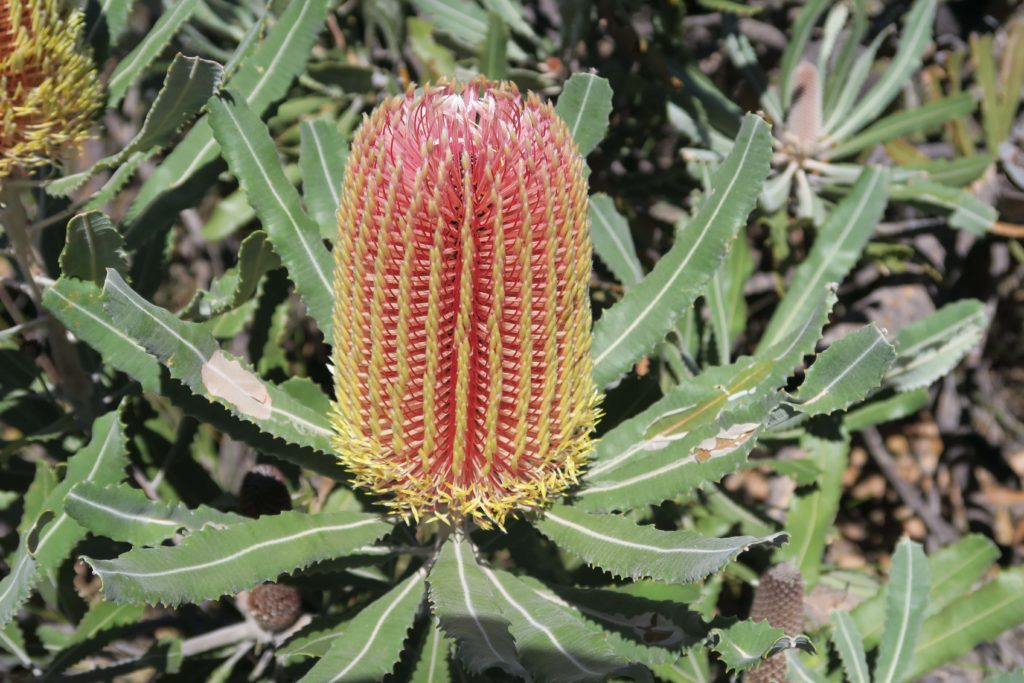
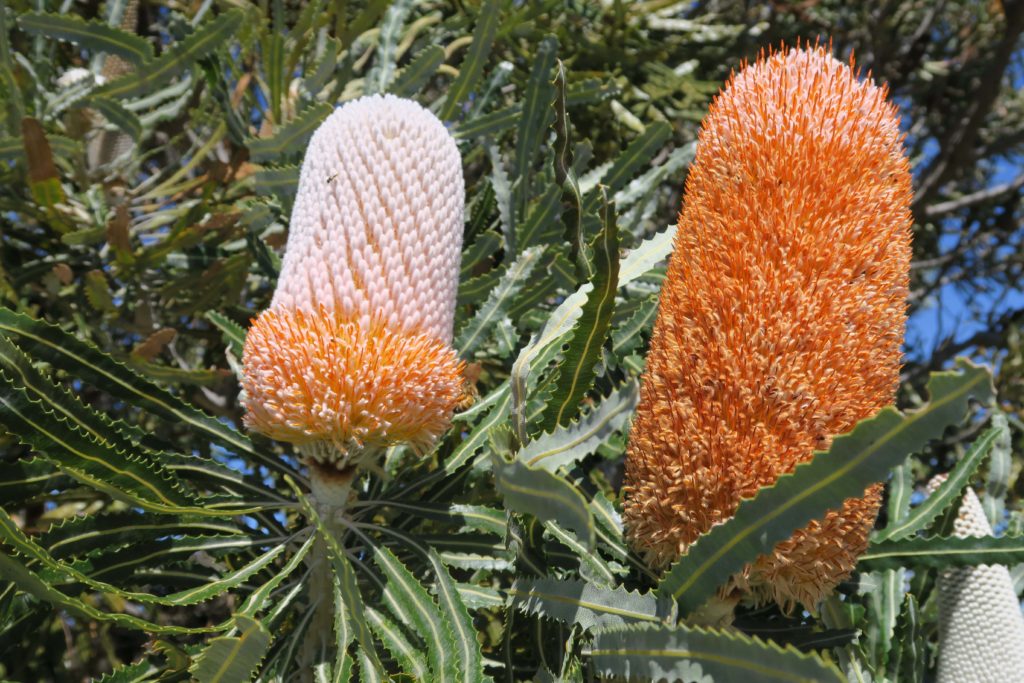
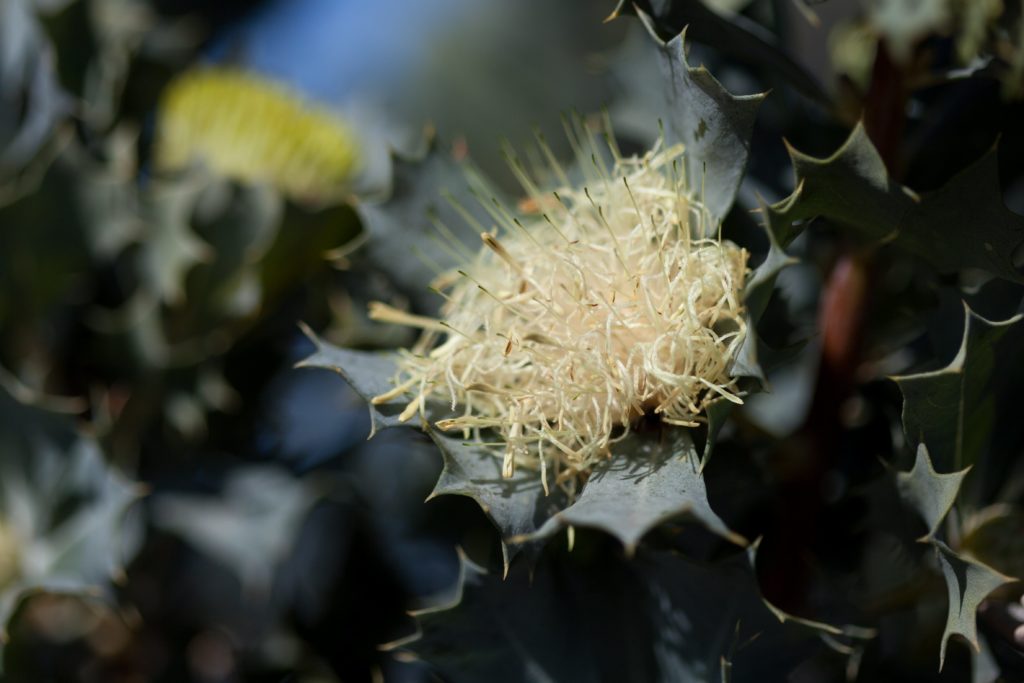
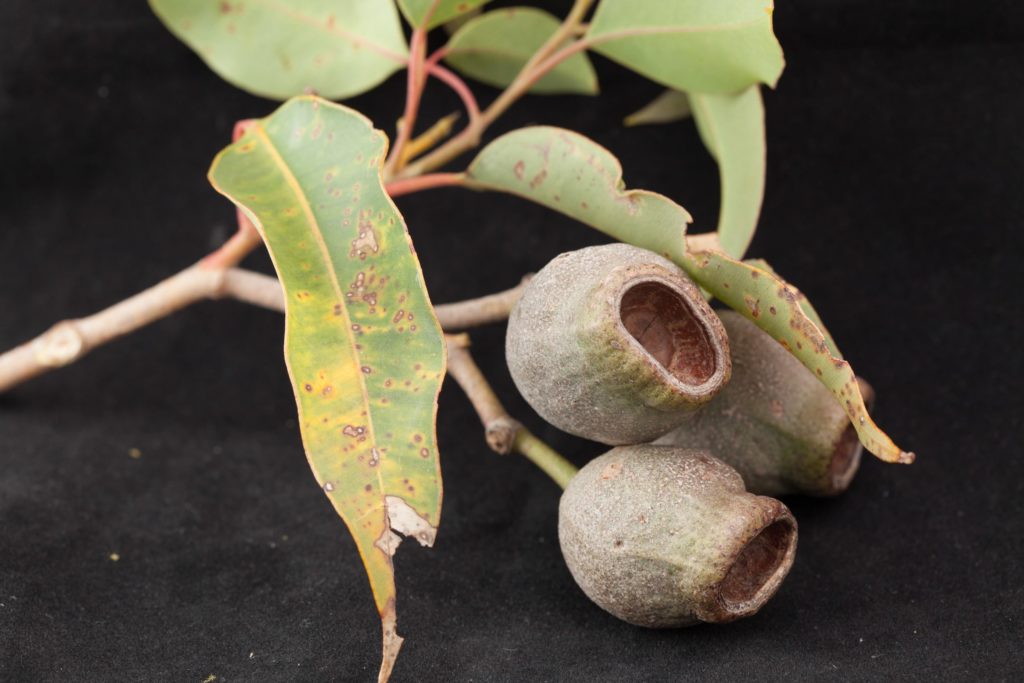
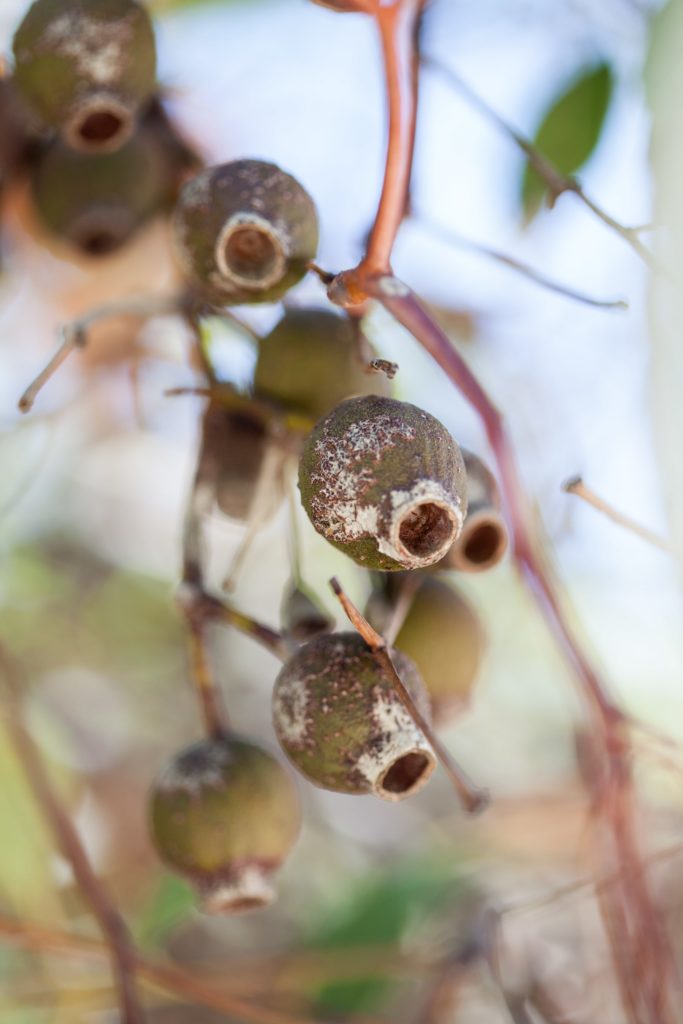
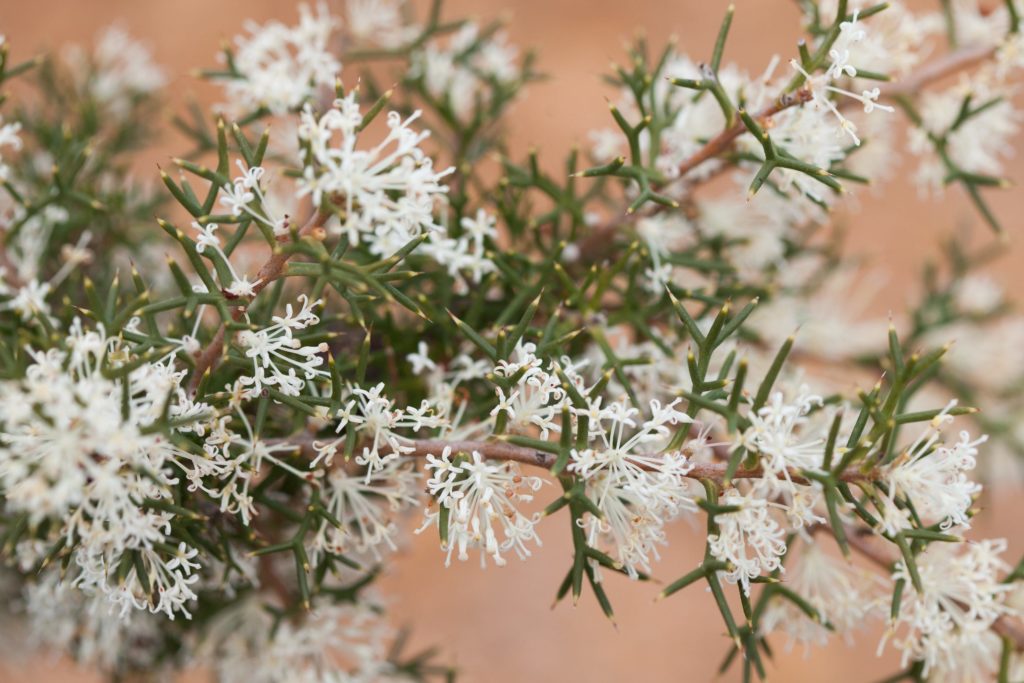












*aboriginal Noongar plant name
A Field Guide to Australian Native Plant Species

The purpose of this Field Guide is to assist with the identification of Australian native plants that are food sources for the three species of wild black cockatoos found in the South West of Western Australia.








